Subgroup
A group of units produced under the same set of conditions. Subgroups
(or rational subgroups) are meant to represent a "snapshot"
of the process. Therefore, they must be taken close together in time but
still be independent of each other. For example, a die cut machine produces
100 plastic parts per hour. The quality engineer measures five randomly
selected parts at the beginning of every hour. Each sample of five parts
is a subgroup.
Use subgroups to separate the two types of variation in a process:
· Within subgroup:
the variation among measurements within subgroups; also known as common
cause variation.
· Between subgroup:
the variation between subgroups that may be caused by specific identifiable
factors, or special causes.
|
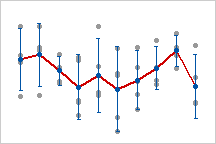
|
This individual value plot displays the values of the
samples taken from the die cut machine. Each vertical line of gray symbols
represents values in a subgroup. The blue intervals represent the within
subgroup variation, and the red mean connect line represents the between
subgroup variation. |
To improve process quality, you should make an effort to eliminate between
subgroup variation and reduce within subgroup variation.
