overview
Minitab computes three measures of accuracy of the fitted model: MAPE, MAD, and MSD for each of the simple forecasting and smoothing methods. For all three measures, the smaller the value, the better the fit of the model. Use these statistics to compare the fits of the different methods.
MAPE, or Mean Absolute Percentage Error, measures the accuracy of fitted time series values. It expresses accuracy as a percentage.
![]()
where yt
equals the actual value, ![]() t
equals the fitted value, and n equals the number of observations.
t
equals the fitted value, and n equals the number of observations.
MAD, which stands for Mean Absolute Deviation, measures the accuracy of fitted time series values. It expresses accuracy in the same units as the data, which helps conceptualize the amount of error.
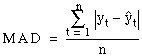
where yt
equals the actual value, ![]() t
equals the fitted value, and n equals the number of observations.
t
equals the fitted value, and n equals the number of observations.
MSD stands for Mean Squared Deviation. MSD is always computed using the same denominator, n, regardless of the model, so you can compare MSD values across models. MSD is a more sensitive measure of an unusually large forecast error than MAD.
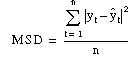
where yt
equals the actual value, ![]() t
equals the forecast value,
and n equals the number of forecasts.
t
equals the forecast value,
and n equals the number of forecasts.