|
|
Analyze Factorial DesignEffects Plots - Normal Effects Plot |
Use a normal effects plot to compare the relative magnitude and the statistical significance of both main and interaction effects. Minitab draws a line to indicate where the points would be expected to fall if all effects were zero. Points that do not fall near the line usually signal significant effects. Such effects are larger and generally further from the fitted line than unimportant effects. By default, Minitab uses an a-level of 0.05 and labels any effect that is significant.
Example Output |
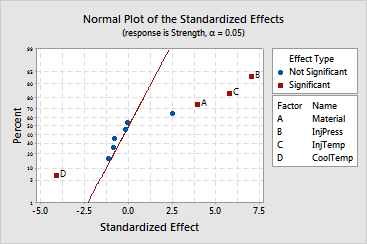
Interpretation |
|
For the insulation data, all four main effects are significant (a = 0.05). Injection pressure (B) has the largest standardized effect.
In addition, the plot indicates the direction of the effect. Material (A), injection pressure (B), and injection temperature (C) all have positive standardized effects. This means that when you change from the low level to the high level of the factor, the response increases. Cooling temperature (D) has a negative effect. This means that when you change from the low level to the high level of the factor, the response decreases.