|
|
Binary Logistic RegressionResidual Plots - Residuals versus order |
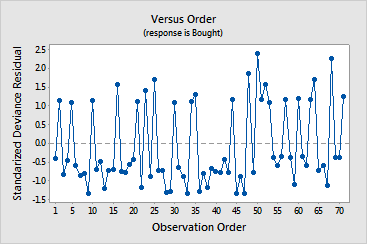
This graph plots the residuals in the order of the corresponding observations. The plot is useful when the order of the observations may influence the results, which can occur when data are collected in a time sequence or in some other sequence, such as geographic area. This plot can be particularly helpful in a designed experiment in which the runs are not randomized.
The residuals in the plot should fluctuate in a random pattern around the center line. Examine the plot to see if any correlation exists between error terms that are near each other. Correlation among residuals may be signified by:
Example Output |
Interpretation |
|
For the cereal data, the residuals alternate relatively quickly. From 36 to 43, 8 customers in a row did not buy the cereal. A series of 8 is not unusual when about 70% of the customers did not buy the cereal, but the cereal company could review the data to see if the customers in the series have common traits.