|
|
Stability StudyResidual Plots - Normal Probability Plot of the Residuals |
This graph plots the residuals versus their expected values when the distribution is normal. The residuals from the analysis should be normally distributed. In practice, for data that have a large number of observations, moderate departures from normality do not seriously affect the results.
The normal probability plot of the residuals should roughly follow a straight line. Use this plot to look for the following patterns:
|
This pattern... |
Indicates... |
|
Not a straight line |
|
|
Curve in the tails |
|
|
A point that is far away from the line |
An outlier |
|
Changing slope |
If your data have fewer than 50 observations, the plot may display curvature in the tails even if the residuals are normally distributed. As the number of observations decreases, the probability plot may show even greater variation and nonlinearity. Use the normal probability plot and goodness-of-fit tests to assess the normality of residuals in small data sets.
If your data do not follow a normal distribution, you may want to consider transforming the data using the Box-Cox transformation.
If batch is a random factor, and the final model includes the batch by time interaction, then the variance of the marginal residuals depends on the time variable and may not be constant. You can use the conditional residuals to check the normality of the error term in the model.
Example Output |
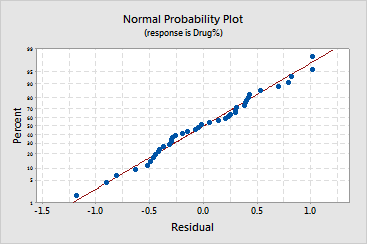
Interpretation |
For the pill data, the residuals appear to follow a straight line. This indicates that the residuals follow a normal distribution.