main topic interpreting results session command see also
The staff at a hospital chain records the number of medication errors each week. Examples of errors include delivering medication at the wrong time, delivering the wrong dose, and delivering the wrong medication.
The average subgroup size is 7500. Because of the large subgroup size, the staff want to determine whether to use a Laney U' chart.
1 Open the worksheet MEDICATIONERRORS.MTW.
2 Choose Stat > Control Charts >Attributes Charts > U Chart Diagnostic.
3 In Variables, enter Errors.
4 In Subgroup sizes, enter Patients. Click OK.
Graph window output
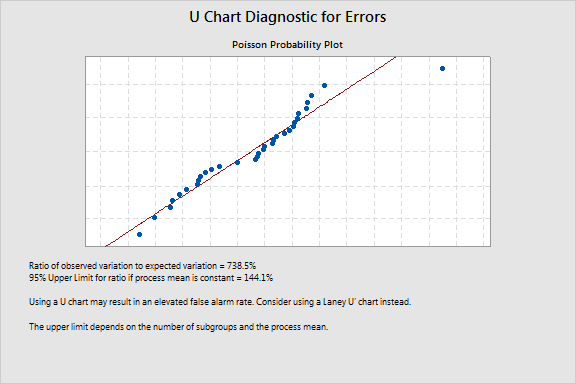
The high ratio of observed variation to expected variation, 738.5%, suggests overdispersion. Overdispersion can cause points on a traditional U chart to appear to be out of control when they are not. To correct for overdispersion, use a Laney U' chart.
To see the same data plotted on both a traditional U chart and a Laney U' chart, see Comparing traditional U charts and Laney U' charts.